Accreditation
In the United States, accreditation is the primary process for assuring and improving the quality of higher education institutions. Accreditation is a self-regulatory, peer review process based on rigorous standards. Although common standards are articulated for participating institutions, they are interpreted in the context of each institution’s unique characteristics and mission.
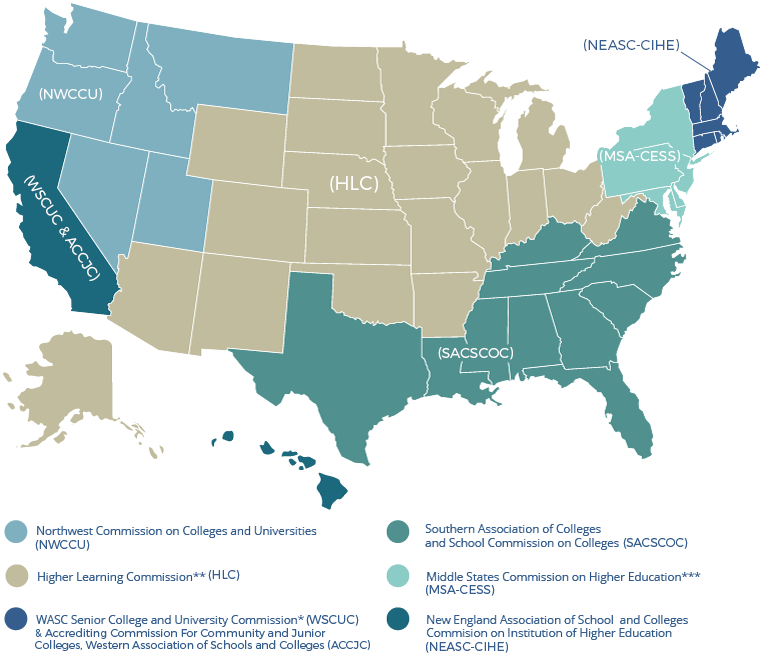
Colleges and universities as are reviewed by institutional accreditors that represent six geographic regions of the country, who coordinate their efforts through the Council of Regional Accrediting Commissions (C-RAC). Baylor University's institutional accreditor is the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC).
In addition, specific academic programs may have program accreditors that focus on measures of quality associated with their particular academic discipline or field. These program commissions are in turn reviewed by the Council on Higher Education Agencies (CHEA).
Although these accreditation commissions are non-governmental agencies, they do review some federal policies for compliance, and serve as a mechanism for authorizing federal financial aid through the U.S. Department of Education (USDE).
For Additional Information on Accreditation: